By David Snowball
Dear friends,
April started well, with the super-rich losing more money in a week than I can even conceive of. Bloomberg reports that the 20 wealthiest people on Earth lost a combined $9.1 billion in the first week of April as renewed concerns that Europe’s debt crisis might worsen drove the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index to its largest decline of 2012. Bill Gates, a year older than me, lost $558.1 million on the week. (World’s Richest Lose $9 Billion as Global Markets Decline).
I wonder if he even noticed?
Return of the Giants
Mark Jewell, writing for the AP, celebrated the resurgence of the superstar managers (Star Fund Managers Recover Quickly from Tough 2011). He writes, “A half dozen renowned managers are again beating their peers by big margins, after trailing the vast majority last year. Each is a past winner of Morningstar’s manager of the year award in his fund category, and four have been honored as top manager of the decade.” Quick snapshots of Berkowitz, Miller and Bill Gross follow, along with passing mention of Brent Lynn of Janus Overseas Fund (JDIAX), Michael Hasenstab of Templeton Global Bond (TPINX) and David Herro of Oakmark International (OAKIX).
A number of funds with very good long-term records were either out-of-step with the market or made bad calls in 2011, ending them in the basement. There are 54 four- or five-star rated funds that tanked in 2011; that is, that trailed at least 90% of their peers. Of those, 23 – 43% of the group – rebounded sharply this year and ended up with 10% returns for the year, through 4/30/11. The rest of the worst-to-first roster:
American Century Zero Coupon 2015 and 2020
Fairholme
Federated International Leader
Jones Villalta Opportunity
SEI Tax-Exempt Tax-Advantaged
Fidelity Advisor Income Replacement 2038, 2040 and 2042
JHancock3 Leveraged Companies
Templeton Global Total Return CRM International Opportunity
Fidelity Capital & Income
REMS Real Estate Value Opportu
Templeton Global Bond and Maxim Templeton Global Bond
Catalyst/SMH Total Return Income
Fidelity Leveraged Company Stock
ING Pioneer High Yield
Templeton International Bond
API Efficient Frontier Income
Hartford Capital Appreciation
PIMCO Total Return III
Before we become too comfortable with the implied “return to normal, we really can trust The Great Men again,” we might also look at the roster of great funds that got hammered in 2011 and are getting hammered again in 2012. Brian Barash at Cambiar Aggressive Value, Leupp and Ronco (no, not the TV gadgets guy) at Lazard U.S. Realty Income Open, The “A” team at Manning & Napier Pro-Blend Maximum Term and Whitney George & company at Royce Micro-Cap range from the bottom 2 – 25% of their peer groups.
Other former titans – Ariel (ARGFX), Clipper (CFIMX, a rare two-star “Gold” fund), Muhlenkamp Fund (MUHLX), White Oak Growth (WOGSX) – seem merely stuck in the mud.
“A Giant Sucking Sound,” Investor Interest in Mutual Funds . . .
and a lackadaisical response from the mutual fund community.
Apropos my recent (and ongoing) bout with the flu, we’re returning to the odd confluence of the Google Flu tracker and the fate of the fund industry. In October 2011, we posted our first story using the Google Trends data, the same data that allows Google to track incidence of the flu by looking at the frequency and location of flu-related Google searches. In that article, we included a graph, much like the one below, of public interest in mutual funds. Here was our original explanation:
That trend line reflects an industry that has lost the public’s attention. If you’ve wondered how alienated the public is, you could look at fund flows – much of which is captive money – or you could look at a direct measure of public engagement. The combination of scandal, cupidity, ineptitude and turmoil – some abetted by the industry – may have punched an irreparable hole in industry’s prospects.
This is a static image of searches in the U.S. for “mutual funds,” from January 2004 to April 2012.
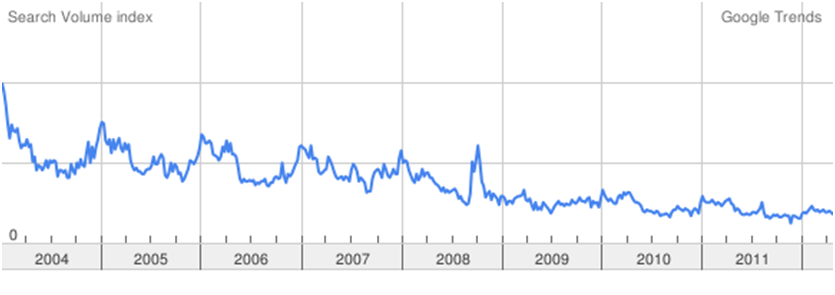
And it isn’t just a retreat from investing and concerns about money. We can separately track the frequency of “mutual funds” against all finance-related searches, which is shown on this live chart:
In brief, the industry seems to have lost about 75% of its mindshare (sorry, it’s an ugly marketing neologism for “how frequently potential buyers think about you”).
That strikes me as “regrettable” for Fidelity and “potentially fatal” for small firms whose assets haven’t yet reached a sustainable level.
I visit a lot of small fund websites every month, read more shareholder communications than I care to recall and interview a fair number of managers. Here’s my quick take: a lot of firms materially impair their prospects for survival by making their relationship with their shareholders an afterthought. These are the folks who take “my returns speak for themselves” as a modern version of “Build a better mousetrap, and the world will beat a path to your door” (looks like Emerson actually did say it, but in a San Francisco speech rather than one of his published works).
In reality, your returns mumble. You’re one of 20,000 datapoints and if you’re not a household name, folks aren’t listening all that closely.
According to Google, the most popular mutual-fund searches invoke “best, Vanguard (three variants), Fidelity (three variants), top, American.”
On whole, how many equity managers do you suppose would invest in a company that had no articulated marketing strategy or, at best, mumbled about the quality of their mousetraps?
And yet, this month alone, in the course of my normal research, I dealt with four fund companies that don’t even have working email links on their websites and several more whose websites are akin to a bunch of handouts left on a table (one or two pages, links to mandatory documents and a four-year-old press release). And it’s regrettably common for a fund’s annual report to devote no more than a paragraph or two to the fund itself.
There are small operations which have spectacularly rich and well-designed sites. I like the Observer’s design, all credit for which goes to Anya Zolotusky of Darn Good Web Design. (Anya’s more interesting than you or me; you should read her bio highlights on the “about us” page.) I’ve been especially taken by Seafarer Funds new site. Three factors stand out:
- The design itself is clear, intuitive and easily navigated;
- There’s fresh, thoughtful content including manager Andrew Foster’s responses to investor questions; and,
- Their portfolio data is incredibly rich, which implies a respect for the active intelligence and interest of their readers.
Increasingly, there are folks who are trying to make life easier for small to mid-sized firms. In addition to long established media relations firms like Nadler & Mounts or Kanter & Company, there are some small firms that seem to be seeking out small funds. I’ve had a nice exchange with Nina Eisenman of FundSites about her experience at the Mutual Fund Education Alliance’s eCommerce show. Apparently some of the big companies are designing intriguing iPad apps and other mobile manifestations of their web presence while representatives of some of the smaller companies expressed frustration at knowing they needed to do better but lacking the resources.
 “What we’re trying to do with FundSites is level the playing field so that a small or mid-sized fund company with limited resources can produce a website that provides investors and advisors with the kind of relevant, timely, compliant information the big firms publish. Seems like there is a need for that out there.”
“What we’re trying to do with FundSites is level the playing field so that a small or mid-sized fund company with limited resources can produce a website that provides investors and advisors with the kind of relevant, timely, compliant information the big firms publish. Seems like there is a need for that out there.”
I agree but it really has to start at the top, with managers who are passionate about what they’re doing and about sharing what they’ve discovered.
Barron’s on FundReveal: Meh
Speaking of mousetraps, Barron’s e-investing writer Theresa Carey dismissed FundReveal as “a lesser mousetrap” (04/21/12). She made two arguments: that the site is clunky and that she didn’t locate any commodity funds that she couldn’t locate elsewhere. Her passage on one of the commodity funds simultaneously revealed both the weakness in her own research and the challenge of using the FundReveal system. She writes:
The top-ranked fund from Fidelity over the past three years is the Direxion Monthly Commodity Bull 2X (DXCLX). While it gets only two Morningstar stars, FundReveal generally likes it, awarding a “B” risk-return rating, second only to “A.” Scouring its 20,000-fund database, FundReveal finds just 61 funds that performed better than the Fidelity pick. (emphasis mine)
Here’s the problem with Theresa’s research: FundReveal does not rank funds on a descending scale of A, B, C, and D. Each of the four quadrants in their system gets a letter designation: “A” is “higher return, lower risk” and “B” is higher return, higher risk.” Plotted in the “B” quadrant are many funds, some noticeably riskier than the others. Treating “B” as if it were a grade on a junior high report card is careless and misleading.
And I’m not even sure what she means by “just 61 funds … performed better” since she’s looking at simple absolute returns over three years or FundReveal’s competing ADR calculation. In either case, we’d need to know why that’s a criticism. Okay, they found 61 superior funds. And so … ?
Her article does simultaneously highlight a challenge in using the FundReveal system. For whatever its analytic merits, the site is more designed for folks who love spreadsheets than for the average investor and the decision to label the quadrants with A through D does carry the risk of misleading casual users.
The Greatest Fund that’s not quite a Fund Anymore
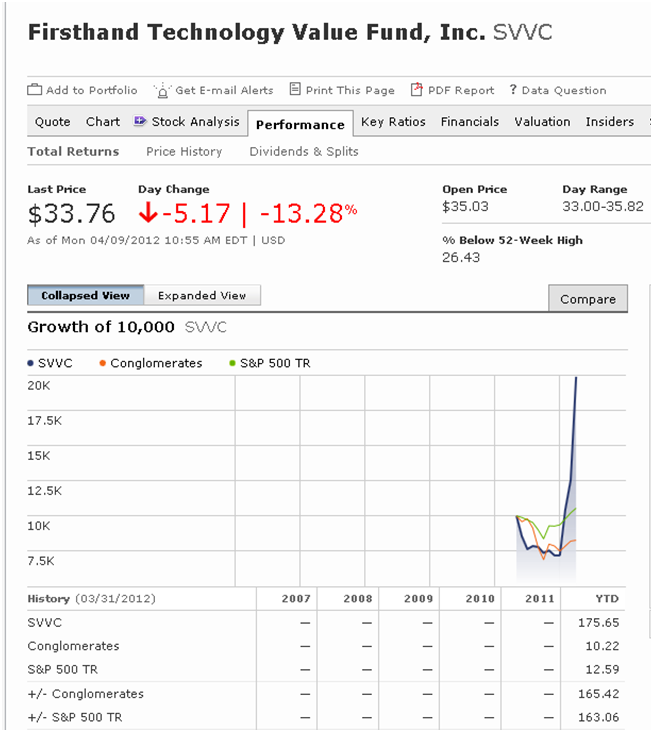
In researching the impending merger of two Firsthand Technology funds (recounted in our “In Brief” section), I came across something that had to be a typo: a fund that had returned over 170% through early April. As in, 14 weeks, 170% returns.
No typo, just a familiar name on a new product. Firsthand Technology Value Fund, despite having 75% of their portfolio in cash (only $15.5 of $68.4 million was invested), peaked at a 175% gain.
What gives? At base, irrational exuberance. Firsthand Technology Value was famous in the 1990s for its premise – hire the guys who work in Silicon Valley and who have firsthand knowledge of it to manage your investments – and its performance. In long-ago portfolio contests, the winner routinely was whoever had the most stashed in Tech Value.
The fund ran into performance problems in the 2000s (duh) and legal problems in recent years (related to the presence of too many illiquid securities in the portfolio). As a result, it transformed into a closed-end fund investing solely in private securities in early 2011. It’s now a publicly-traded venture capital fund that invests in technology and cleantech companies that just completed a follow-on stock offering. The fund, at last report, held stakes in just six companies. But when one of those companies turned out to be Facebook, a bidding frenzy ensued and SVVC’s market price lost all relationship to the fund’s own estimated net asset value. The fund is only required to disclose its NAV quarterly. At the end of 2011, it was $23.92. At the end of the first quarter of 2012, it was $24.56 per share.
Right: NAV up 3%, market price up 175%.
In April, the fund dropped from $46.50 to its May 1 market price, $26.27. Anyone who held on pocketed a gain of less than 10% on the year, while folks shorting the stock in April report gains of 70% (and folks who sold and ran away, even more).
It’s a fascinating story of mutual fund managers returning to their roots and investors following their instincts; which is to say, to rush off another cliff.
Four Funds and Why They’re Really Worth Your While
Each month, the Observer profiles between two and four mutual funds that you likely have not heard about, but really should have. Our “Most intriguing new funds: good ideas, great managers” do not yet have a long track record, but have other virtues which warrant your attention. They might come from a great boutique or be offered by a top-tier manager who has struck out on his own. The “most intriguing new funds” aren’t all worthy of your “gotta buy” list, but all of them are going to be fundamentally intriguing possibilities that warrant some thought. Two intriguing newer funds are:
Amana Developing World Fund (AMDWX): Amana, which everyone knew was going to be cautious, strikes some as near-comatose. We’ve talked with manager Nick Kaiser about his huge cash stake and his recent decision to begin deploying it. This is an update on our May 2011 profile.
FMI International (FMIJX): For 30 years, FMI has been getting domestic stock investing right. With the launch of FMI International, they’ve attempted to “extend their brand” to international stocks. So far it’s been performing about as expected, which is to say, excellently
The “stars in the shadows” are all time-tested funds, many of which have everything except shareholders.
Artisan Global Value (ARTGX): can you say, “it’s about time”? While institutional money has long been attracted to this successful, disciplined value strategy, retail investors began to take notice just in the past year. Happily, the strategy has plenty of capacity remaining. This is an update on our May 2011 profile.
LKCM Balanced (LKBAX): LKCM Balanced (with Tributary Balanced, Vanguard Balanced Index and Villere Balanced) is one of a small handful of consistently, reliably excellent balanced funds. The good news for prospective shareholders is that LKCM slashed the minimum investment this year, from $10,000 to $2,000, while continuing its record of great, risk-conscious performance.
The Best of the Web: Curated Financial News Aggregators
Our third “Best of the Web” feature focuses on human-curated financial news aggregators. News aggregators such as Yahoo! News and Google News are wildly popular. About a third of news users turn to them and Google reports about 100,000 clicks per minute at the Google News site.
The problem with aggregators such as Google is that they’re purely mechanical; the page content is generated by search algorithms driven by popularity more than the significance of the story or the seriousness of the analysis.
In this month’s “Best of the Web,” Junior and I test drove a dozen financial news aggregators, but identified only two that had consistently excellent, diverse and current content. They are:
Abnormal Returns: Tadas Viskanta’s six year old venture, with its daily linkfests and frequent blog posts, is for good reason the web’s most widely-celebrated financial news aggregator.
Counterparties: curated by Felix Salman and Ryan McCarthy, this young Reuter’s experiment offers an even more eclectic mix than AR and does so with an exceptionally polished presentation.
As a sort of mental snack, we also identified two cites that couldn’t quite qualify here but that offered distinctive, fascinating resources: Smart Briefs, a sort of curated newsletter aggregator and Fark, an irreverent and occasionally scatological collection of “real news, real funny.” You can access Junior’s column from “The Best” tab or here. Columns in the offing include coolest fund-related tools, periodic tables (a surprising number), and blogs run by private investors.
We think we’ve done a good and honest job but Junior, especially, would like to hear back from readers about how the feature works for you and how to make it better, about sites we’re missing and sites we really shouldn’t miss. Drop us a line. We read and appreciate everything and respond to as much as we can.
A “Best of” Update: MoneyLife with Chuck Jaffe Launches
 Chuck Jaffe’s first episode of the new MoneyLife show aired April 30th. The good news: it was a fine debut, including a cheesy theme song and interviews with Bill O’Neil, founder of Investor’s Business Daily and originator of the CAN-SLIM investing system, and Tom McIntyre. The bad news: “our Twitter account was hijacked within the 48 hours leading up to the show, which is one of many adventures you don’t plan for as you start something like this.” Assuming that Chuck survives the excitement of his show’s first month, Junior will offer a more-complete update on June 1. For now, Chuck’s show can be found here.
Chuck Jaffe’s first episode of the new MoneyLife show aired April 30th. The good news: it was a fine debut, including a cheesy theme song and interviews with Bill O’Neil, founder of Investor’s Business Daily and originator of the CAN-SLIM investing system, and Tom McIntyre. The bad news: “our Twitter account was hijacked within the 48 hours leading up to the show, which is one of many adventures you don’t plan for as you start something like this.” Assuming that Chuck survives the excitement of his show’s first month, Junior will offer a more-complete update on June 1. For now, Chuck’s show can be found here.
Briefly noted …
Steward Capital Mid-Cap Fund (SCMFX), in a nod to fee-only financial planners, dropped its sales load on April 2. Morningstar rates it as a five-star fund (as of 4/30/12) and its returns over the past 1-, 3- and 5-year periods are among the best of any mid-cap core fund. The investment minimum is $1000 and the expense ratio is 1.5% on $35 million in assets.
Grandeur Peak Global Advisors recently passed $200 million in assets under management. Roughly $140M is in Global Opportunities (GPGOX/GPGIX) and $60M is in International Opportunities (GPIOX/GPIIX). That’s a remarkable start for funds that launched just six months ago.
Calamos is changing the name of its high-yield fixed-income fund to Calamos High Income from Calamos High Yield (CHYDX) on May 15, 2012 because, without “income” in the name investors might think the fund focused on high-yielding corn hybrids (popular here in Iowa).
T. Rowe Price High Yield (PRHYX) and its various doppelgangers closed to new investors on April 30, 2012.
Old Mutual Heitman REIT is in the process of becoming the Heitman REIT Fund, but I’m not sure why I’d care.
ING’s board of directors approved merging ING Index Plus SmallCap (AISAX) into ING Index Plus MidCap (AIMAX) on or about July 21, 2012. The combined funds will be renamed ING SMID Cap Equity. In addition, ING Index Plus LargeCap (AELAX) was approved to merge into ING Corporate Leaders 100 (IACLX) on or about June 28, 2012. Let’s note that ING Corporate Leaders 100 is a different, and distinctly inferior fund, than ING Corporate Leaders Trust “B”.
Huntington New Economy Fund (HNEAX), which spent most of the last decade in the bottom 5-10% of mid cap growth funds, is being merged into Huntington Mid Corp America Fund (HUMIX) in May 2012. HUMIX is less expensive than HNEAX, though still grievously overpriced (1.57%) for its size ($139 million in assets) and performance (pretty consistently below average).
The Firsthand Funds are moving to merge Firsthand Technology Leaders Fund (TLFQX) into Firsthand Technology Opportunities Fund TEFQX). The investment objective of TLF is identical to that of TOF and the investment risks of TLF are substantially similar to those of TOF. TLF is currently managed solely by Kevin Landis (TLF was co-managed by Kevin Landis and Nick Schwartzman from April 30, 2010 to December 13, 2011).
The $750 million Delaware Large Cap Value Fund is being merged into the $750 million Delaware Value® Fund, which “does not require shareholder approval, and you are not being asked to vote.”
The reorganization has been carefully reviewed by the Trust’s Board of Trustees. The Trustees, most of whom are not affiliated with Delaware Investments®, are responsible for protecting your interests as a shareholder. The Trustees believe the reorganization is in the best interests of the Funds based upon, among other things, the following factors:
Shareholders of both Funds could benefit from the combination of the Funds through a larger pool of assets, including realizing possible economies of scale . . .
Uhhh . . . notes to the “Board of Trustees [who] are responsible for protecting [my] interests”: (1) it’s “who,” not “whom.” (2) If Delaware Value’s asset base is doubling and you’re anticipating “possible economies of scale,” why didn’t you negotiate a decrease in the fund’s expense ratio?
Snow Capital All Cap Value Fund (SNVAX) is being closed and liquidated as of the close of business on May 14, 2012. The fund, plagued by high expenses and weak performance, had attracted only $3.7 million despite the fact that the lead manager (Richard Snow) oversees $2.6 billion.
Likewise, Dreyfus Dynamic Alternatives Fund and Dreyfus Global Sustainability Fund were both liquidated in mid-April.
Forward seems to be actively repositioning itself away from “vanilla” products and into more-esoteric, higher cost funds. In March, Forward Banking and Finance Fund and Forward Growth Fund were sold to Emerald Advisers, who had been running the funds for Forward, rebranded as Emerald funds. Forward’s board added International Equity to the dustbin of history on April 30, 2012 and Mortgage Securities in early 2011. Balancing off those departures, Forward also launched four new funds in the past 12 months: Global Credit Long/Short, Select Emerging Markets Dividend, Endurance Long/Short, Managed Futures and Commodity Long/Long.
On April 17, 2012, the Board of Trustees of the ALPS ETF Trust authorized an orderly liquidation of the Jefferies|TR/J CRB Wildcatters Exploration & Production Equity Fund (WCAT), which will be completed by mid-May. The fund drew fewer than $10 million in assets and managed, since inception, to lose a modest amount for its (few) investors.
Effective on June 5, 2012, the equity mix in Manning & Napier Pro-Blend Conservative Term will include a greater emphasis on dividend-paying common stocks and a larger allocation to REITs and REOCs. Their other target date funds are shifting to a modestly more conservative asset allocation.
Nice work if you can get it. Emily Alejos and Andrew Thelen were promoted to become the managers of Nuveen Tradewinds Global All-Cap Plus Fund of April 13. The fund, after the close of business on May 23, 2012, is being liquidated with the proceeds sent to the remaining shareholders. Nice resume line and nothing they can do to goof up the fund’s performance.
News Flash: on April 27, 2012 Wilmington Multi-Manager International Fund (GVIEX), a fund typified by above average risks and expenses married with below average returns, trimmed its management team from 27 managers down to a lean and mean 26 with the departure of Amanda Cogar.
In closing . . .
Thanks to all the folks who supported the Observer in the months just passed. While the bulk of our income is generated by our (stunningly convenient!) link to Amazon, two or three people each month have made direct financial contributions to the site. They are, regardless of the amount, exceedingly generous. We’re deeply grateful, as much as anything, for the affirmation those gestures represent. It’s good to know that we’re worth your time.
In June we’ll continuing updating profiles including Osterweis Strategic Investment (OSTVX – gone from “quietly confident” to “thoughtful”) and Fidelity Global Strategies (FDYSX – skeptical then, skeptical now). We’ll profile a new “star in the shadows,” Huber Small Cap Value (HUSIX) and greet the turbulent summer months by beginning a series of profiles on long/short funds that might be worth the money. June’s profile will be ASTON/River Road Long-Short Fund (ARLSX).
As ever,